0 +
Years Experience
0 +
Materials & Finishes
0 +
Countries Served
0 +
Customers Trusted us
0 %
On Time Delivery
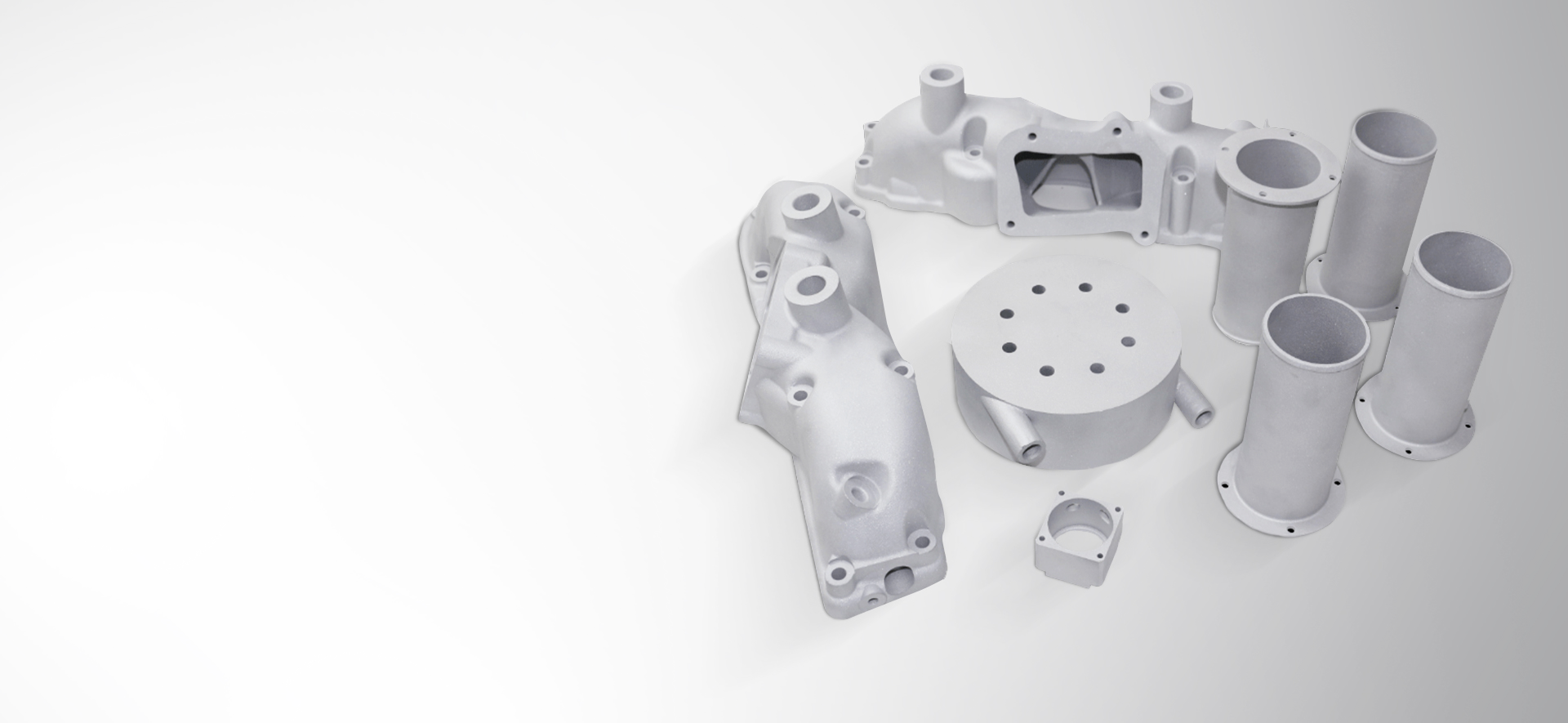
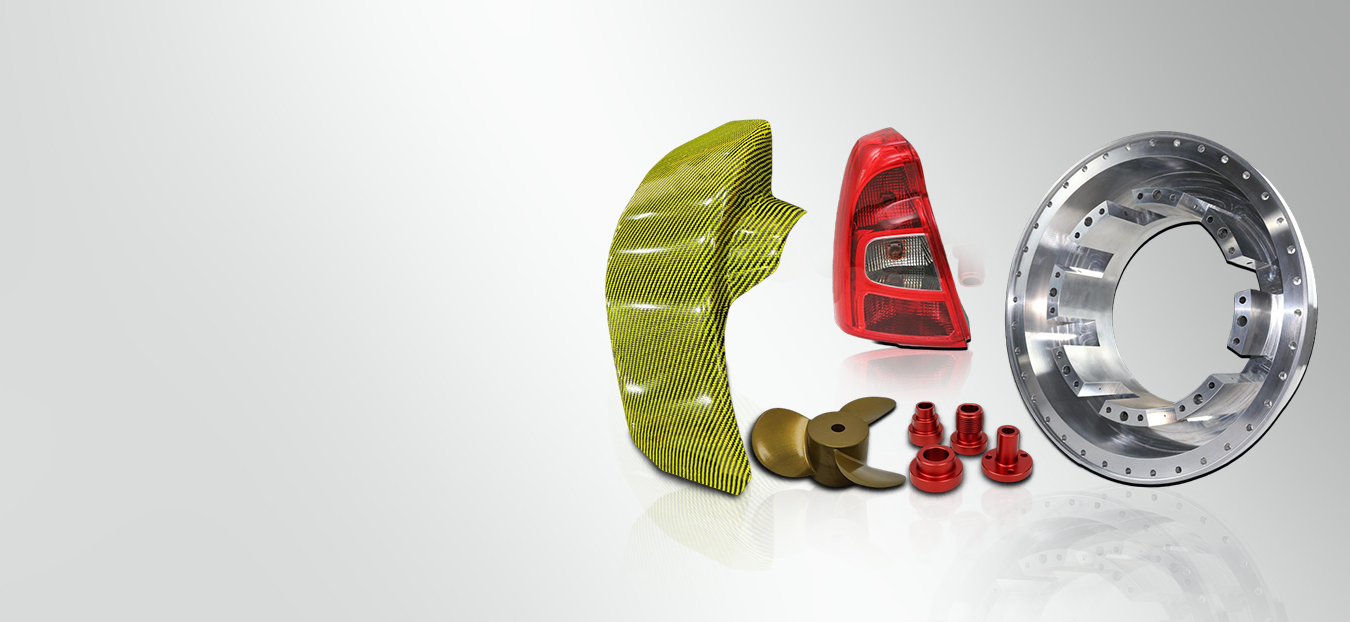
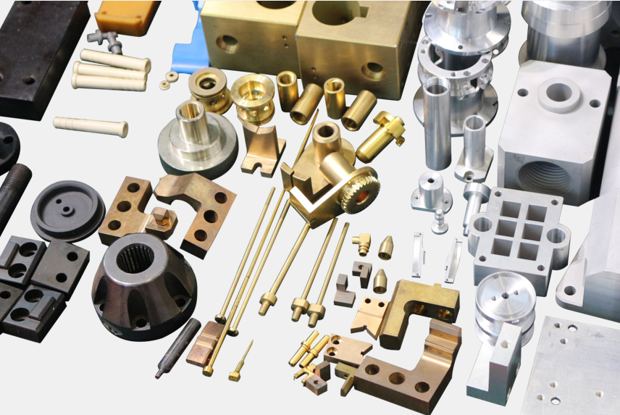
IN3DTEC Manufacturing Capabilities To Meet Your Needs

3D Printing
FDM, SLM, SLA, SLS, DLP, MJF, Ceramic, Sand printing & Casting, Colorful parts. As fast as one day.

CNC Machining
CNC Milling ( 3,4, 5 axis) CNC Turning, EDM. up to ±0.003mm (±0.0001in)

Injection Molding
Insert Molding, Over molding, Low volume Injection Molding. No MOQ, from 1 to 1M parts.

Vacuum Casting/Urethane Casting
ABS, PP, Nylon, PC, TPU/Rubber, Transparent. Best alternative to injection molding for low volume run.

3D Scanning
Low cost to create a CAD file in 1-3 days.The final format be delivered in STL or STEP format.

Carbon Fiber Composites
High-strength, lightweight for durable, precise, and performance-driven engineering applications.

Die Casting
Aluminum/Zinc/Magnesium/Copper. 0.03in walls, 1000+ unit batches.

Sheet Metal
Expert laser cutting, bending, welding & stamping. Fast, highly precise.
From Quote To Delivery
Everything You Need in One Easy-to-use Platform
Our AI-powered online quoting tool delivers prices within seconds and makes order tracking and management effortless. With built-in DFM capabilities, it helps identify design errors early, saving your time and ensuring smoother part production.
No Minimum Quantity
AI-Powered DFM Analysis
Online Order Management
Flexible Lead Time & Shipping Options

Walls are too thin, minimum recommended thickness value is 1.0
Show thin walls
What is the most cost-effective way to make a transparent part?
SLA is a good choice for a prototype. Other options can be vacuum casting and CNC machining.
Can you print titanium, which grage?
We can print Titanium, Grade 5.
Can you ship parts to the united kingdom?
Yes, we can ship parts globally.
what's the tolerance of metal printing?
0.2% X length, +/-0.2mm minimum.
AI-powered & Human Technical
Assistant
Our AI-powered bot instantly assists with material selection, order processing, shipping updates, and other common inquiries. For more personalized support, you can switch to our human customer service team at any time via WhatsApp, Google Meet, Zoom, or Microsoft Teams.

Why Does IN3DTEC Standout?

Various Capabilities
With 400+ machines and over 160 materials and surface finishes, we offer customers a complete one-stop solution for part production

Fast And Affordable
Each order is managed by a dedicated sales representative, while we control costs at every stage to provide our customers with competitive pricing.

Engineering Support
More than just making parts, we deliver value — our designers and machinists support customers throughout the entire workflow.

Quality Assurance
At IN3DTEC, quality is our priority — from raw materials to final inspection, every process is rigorously controlled.
“IN3DTEC is a wholly trusted partner. They help us develop new products more efficiently and quickly. High-quality products and competitive prices are also why we recommend them to more people.” Luis Ford at Leica Medical Product Design Team
Excellent 4.9 out of 5 
Manufacturing Resources
View All
Cool & Useful Things, ideas to 3D Print for November
100 cool & useful 3D Print Projects, Ideas You’ll Love In the ever-evolving world of technology, 3D printing stands out as a game-changing tool that
Read More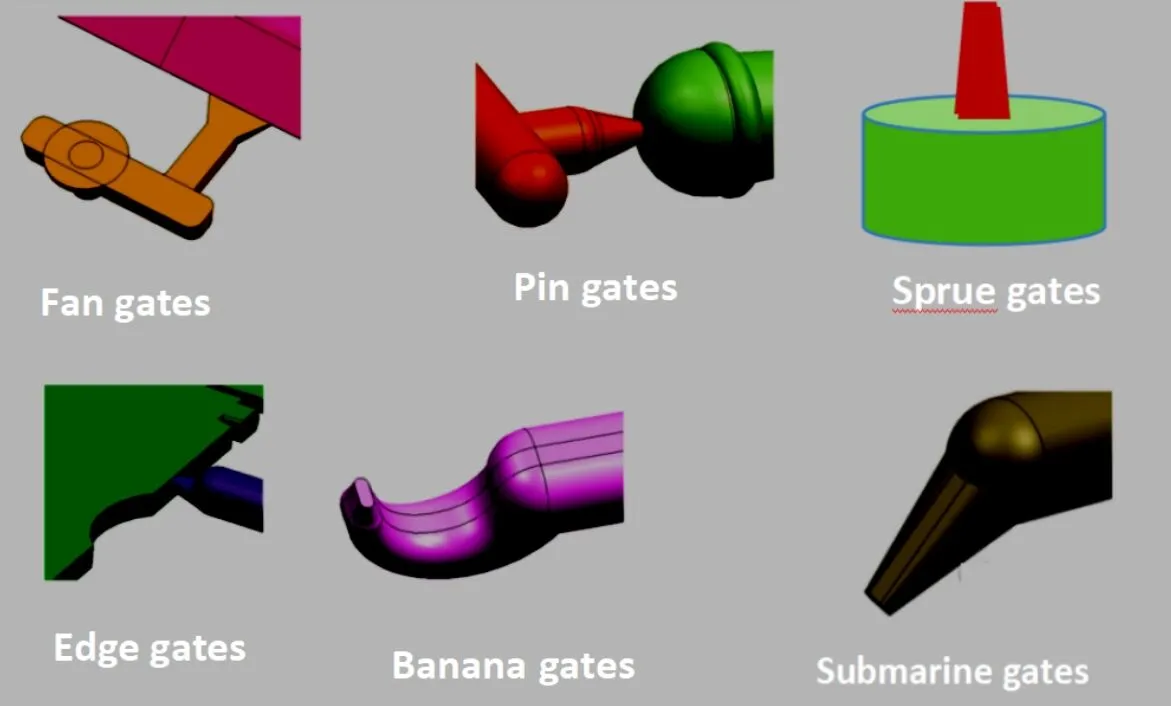
A Comprehensive Guide to Injection Molding Gates
Comprehensive Guide to Injection Molding Gates Introduction: Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process for producing plastic parts with high precision and efficiency. A
Read More
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Material Selection Guide for Low Volume Production
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Material Selection Guide for Low Volume Production In recent years, Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) has emerged as one of the most
Read More
How to design parts for metal 3D Printing
With the gradual popularization of 3D printing, more and more users will directly consider metal printing when producing products, so how to design a product suitable for metal printing? Is anything we should pay attention to? IN3DTEC will analyze the des
Read More
Modernizing Metal Casting with Sand 3D Printing
Modernizing Metal Casting with Sand 3D Printing for centuries, metal casting has been a trusted method to produce strong, complex parts across industries—from automotive and
Read MoreHow to Work With
Upload a CAD File
Simply upload your CAD file

Get Quote with DFM
Get real-time pricing and DFM insights within seconds. Or ask for manual design help.
Manufacturing Begins
Once your order is placed, We’.ll begin production right away, and you can track and manage it anytime from your dashboard
Parts are Shipped
Partnering with FedEx, DHL and UPS, we deliver your parts fast and on time, worldwide


 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Français
Français Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 Русский
Русский 中文
中文