Unveiling the Must-Know Essential Features of Cura Slicer
Cura is a popular slicing software used in 3D printing that allows you to prepare your 3D models for printing. It offers a wide range of features and settings to optimize the printing process and achieve the best possible results. In this blog post, we will explore some essential features in Cura that you need to know.
Content
- Machine settings: Start-Gcode & End-Gocde
- Quality
- Preferences: Expert, Basic, Advanced
- Walls
- Printing Speed
- Support Structures
- Infill Mode & Density
- Travel
- Cooling Speed
- Build Plate adhesion
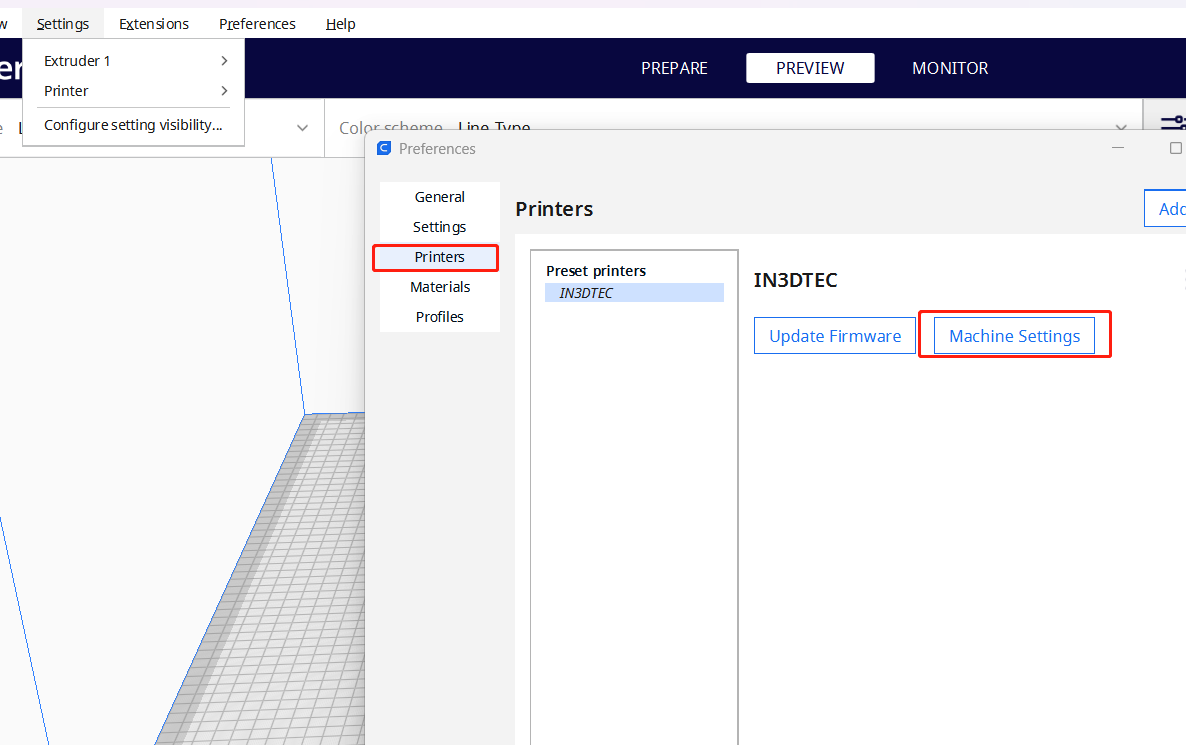
1.Machine settings: Start-Gcode & End-Gcode
Each 3D Printer has different construction dimensions, zeroing methods, and optimum values for retraction. The reasonable setting of the start point and end point of the nozzle will also help the extrusion volume of the filament and avoid scratch after printing. The correct setting is the first step to successful printing. You can ask the 3D Printer manufacturer for this value, and then import it directly.
2.Quality
Quality settings in Cura refer to a set of parameters that allow you to fine-tune the print quality of your 3D prints.
-Layer Height:
The layer thickness directly affects the appearance of the print, the lower the layer thickness, the longer the printing time, the smoother the surface, and the higher the quality.
-Initial line thickness:
The higher the value, the lower the leveling requirements and easier to print
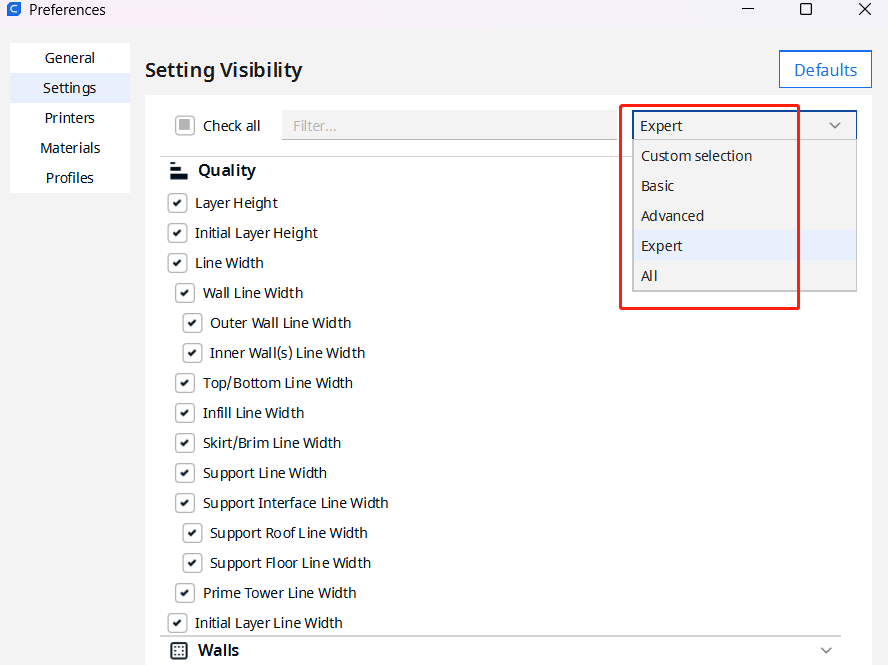
3. Preferences: Expert, Basic, advanced
For beginners, we do not recommend expert mode. advanced mode is a good start, it is enough for most materials like ABS, PLA, PETG.
4.Walls
-Wall line count:
If the settings in quality determine the appearance of the sample. Then the settings in walls have a great influence on the strength of the sample.
Simple understanding, in the case of non-solid printing of the sample, the more wall line count, the stronger the sample. 3 count is good for most of the prints.
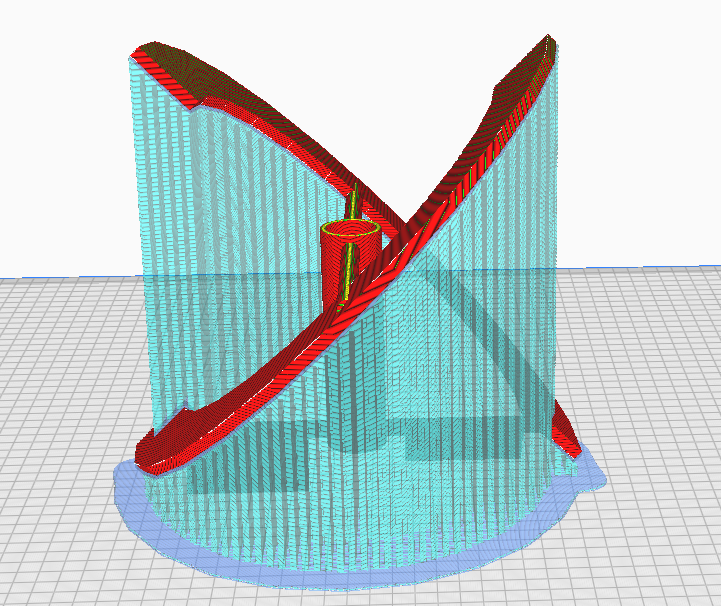
-Z Seam Alignment:
The last thing we want to see is a seam line on the surface of the printed part, which is a defect for 3D printed parts with high appearance requirements. The line is actually the starting point of printing. It’s impossible to avoid it completely, but at least its position can be adjusted, and it can be hidden inside, in a corner or elsewhere. At the same time, it can be improved by increasing the amount of withdrawal and speeding up the withdrawal speed.
5.Printing Speed
-Initial Layer Speed:
The printing speed of the initial layer must be slow and must not be rushed. The failure of most parts is the first layer, because the robustness of the prototype and platform is critical. Slow print speeds allow users to observe problems and make adjustments. Once the first layer is printed, you can enjoy a cup of coffee in peace.
– Other speed:
Different 3D printers have different printing speed mainly depends on mechanical factors such as their motors, screw rods, main boards and so on. It is recommended to consult the manufacturer of the 3D printing equipment before adjustment.
6.Support Structures
-Support Blocker:
Know how to use the Cura Support Blocker is very important. As it can help users reduce unnecessary supports, reduce costs and optimize printing effects.
-Support Pattern:

When it comes to printing complex models or designs with overhangs, support structures are essential for ensuring successful prints. Cura offers a variety of support patterns that provide stability during the printing process and can be easily removed afterward. So it’s also important to know which support type is best for your 3D printed part.
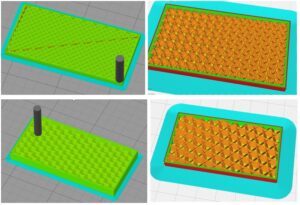
7.Infill Mode & Density
-Infill Pattern:
Cura offers different patterns to fill the internal space, such as grid, lines, triangles, zigzag, and more. Each pattern has its own characteristics in terms of strength, flexibility, and print time.
-Infill Density:
This setting determines the amount of infill material used to fill the object. It is usually specified as a percentage, where higher percentages result in a denser and stronger internal structure. Lower percentages reduce material usage and print time but may sacrifice strength.
-Infill Line Distance:
This setting defines the distance between each infill line. A smaller distance creates a denser infill, while a larger distance reduces print time and material usage. It is important to balance this setting with the nozzle size and layer height for optimal results.
8.Travel
-Retraction:
There are two important parameters in retraction, one is retraction speed, and the other is retraction distance. Proper retraction settings can reduce post-processing time after printing. When the retraction distance is set too low, it may cause material stringing or tiny dots on the surface of the printed object due to excessive material oozing. If the retraction distance is set too high, the material may not flow smoothly, resulting in holes caused by material shortage. The specific values depend on the length of the extrusion module and should be consulted with the 3D Printer manufacturer.
Retraction speed is easy to understand. High speed can cause filament breakage, while low speed can result in material overflow.
-Travel Speed
Travel speed is the speed at which the printhead moves during retraction, and the specific value often depends on the quality of the motor equipped in the printing device. Sometimes, you may hear strange noises coming from a 3D printer even when the axis is feeding smoothly. This is often due to the retraction speed settings. It is recommended to consult the manufacturer of the 3D printer for advice.
9.Cooling Speed
Cooling speed depends on the material, and it is important to note that not all materials require the option of cooling speed, such as ULTEM, PPSF, ABS, PC, etc. However, proper cooling speed can optimize the smoothness of the print.
10. Build Plate Adhesion
-Brim:
Brim is ideal for common plastics: PLA, PETG, ABS
-Raft:
Strongly recommended if you print huge size of ABS, PC. Or high-performance plastics such as PEEK, ULTEM, PPS, PPSF, PC-ABS. The most important point is to control the distance between the print object and the raft properly, avoiding excessive distance that may cause separation during printing, or being too close that they cannot separate after printing. There is no exact value for this point, so it requires multiple trials and experimentation.