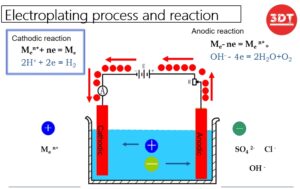
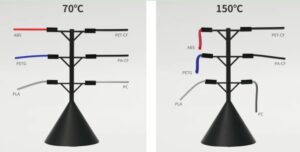
The Whitepaper of CNC Router: Revolutionizing Precision and Efficiency in Manufacturing
Introduction:
CNC routers have emerged as a transformative technology in the manufacturing industry, revolutionizing the way we create intricate designs and prototypes. This whitepaper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of CNC routers, exploring their capabilities, applications, and the benefits they bring to modern manufacturing processes.
CNC Router definition & work principle
What is CNC Router?
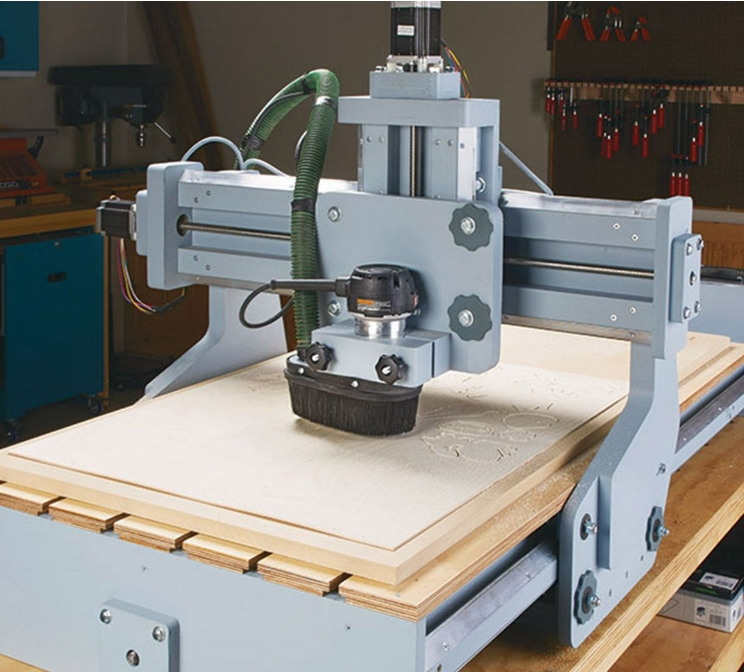
CNC routers can be defined as computer-controlled cutting machines that utilize rotating cutting tools to shape and carve materials with high precision. These machines are equipped with a control system that manages their operation, including the translation of digital designs into machine-readable instructions. By following pre-programmed instructions, CNC routers are able to execute precise movements along multiple axes, allowing for intricate and accurate cuts. The rotating cutting tools, such as router bits or end mills, are attached to a spindle and can be selected based on the specific cutting requirements. This combination of computer control, precise movements, and rotating cutting tools enables CNC routers to achieve exceptional accuracy and repeatability in material shaping and carving processes.
How CNC router works?
CNC routers translate digital designs into physical objects through a process of automated tool movement along multiple axes. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how this translation occurs:
- Digital Design Creation
- CAM Software Preparation
- Toolpath Generation
- G-Code Generation
- G-Code Loading
- Workpiece Setup
- Tool Setup
- Execution of the G-Code Program
- Automated Tool Movement
- Material Shaping and Carving
By automating the tool movement based on the digital design and executing the G-code program, CNC routers are able to transform virtual designs into physical objects with high precision and repeatability.
Applications of CNC Routers:
Woodworking and Furniture Manufacturing:
CNC routers have revolutionized woodworking and furniture manufacturing. They offer precise cutting and shaping capabilities, allowing for intricate designs and complex joinery. With their versatility in working with different wood materials, they streamline batch production and increase efficiency. CNC routers enable customization and design flexibility, while also saving time compared to manual techniques. Integration with CAD/CAM software enhances the design-to-production process. Overall, CNC routers have become indispensable tools for creating high-quality, customized furniture pieces efficiently.
Sign Making and Engraving:
CNC routers are incredibly versatile in the signage industry, offering the ability to create customized signs and intricate engravings with exceptional detail. These machines excel at producing signage that is tailored to specific requirements, allowing for personalized designs, unique shapes, and custom details. With their precision and flexibility, CNC routers enable sign makers to bring intricate visions to life, resulting in visually stunning and highly customized signage solutions. Whether it’s crafting intricate lettering, logos, or decorative engravings, CNC routers provide the versatility needed to achieve exceptional and detailed outcomes in the signage industry.
Prototyping and Rapid Manufacturing:
CNC routers play a crucial role in prototyping by enabling the quick and accurate creation of functional prototypes and models. They offer rapid production, material versatility, and high precision, allowing designers to iterate designs efficiently. CNC routers facilitate the evaluation of form, fit, and functionality, supporting the development of cost-effective and successful products.
Aerospace and Automotive Industries:
CNC routers have significant applications in the aerospace and automotive industries. Here’s an overview of how CNC routers are utilized in these sectors:
Aerospace Industry:
-Composite Component Manufacturing: They can accurately cut and shape composite laminates, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, to create lightweight and durable components used in aircraft structures, interiors, and engine parts.
– Tooling and Molds: CNC routers are employed to produce molds and tooling for aerospace manufacturing processes.
-Prototyping and R&D: CNC routers enable the quick and accurate production of prototypes and models, facilitating the evaluation of new designs, testing of aerodynamic concepts, and validation of manufacturing processes.
-Trimming and Finishing Operations: CNC routers can trim excess material, smooth edges, and create precise cutouts for fasteners, ensuring the components meet the required specifications and tolerances.
Automotive Industry:
-Interior and Exterior Trim Components
-Prototyping and Concept Cars
-Tooling and Fixtures: CNC routers can create molds, jigs, and templates used in stamping, welding, and assembly operations, ensuring accuracy and repeatability in the production of automotive components.
– Customization and Personalization: CNC routers can create unique designs, logos, and patterns on various automotive parts, allowing for personalized touches and branding elements.
Advantages of CNC Routers:
CNC routers offer several advantages in various industries. Here are some key advantages of using CNC routers:
- Precision: CNC routers deliver high levels of precision and accuracy in cutting, carving, and shaping operations. They can consistently reproduce complex designs and intricate details, ensuring uniformity and quality in the final product.
- Efficiency:CNC routers automate the manufacturing process, resulting in increased efficiency and productivity. Once the design and toolpaths are programmed, the router can operate continuously, reducing production time and maximizing output.
- Versatility: CNC routers are versatile machines that can work with a wide range of materials, including wood, plastics, metals, and composites. This versatility allows for diverse applications across industries, from woodworking and signage to aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
- Complex Designs:CNC routers enable the creation of complex designs and intricate patterns that may be challenging or time-consuming to achieve with manual methods. They can execute intricate cuts, engravings, and 3D contours, expanding design possibilities and enhancing creativity.
- Reproducibility: CNC routers ensure reproducibility in production. Once a design is programmed, the router can replicate the same cuts and shapes consistently, ensuring uniformity across multiple pieces or batches.
- Automation and Reduced Labor:CNC routers automate various tasks, reducing the need for manual labor. This leads to cost savings, increased safety, and the ability to focus human resources on other crucial aspects of the manufacturing process.
- Prototyping and Iteration:CNC routers facilitate rapid prototyping and iteration. Design changes can be easily implemented in the digital design, and the CNC router can quickly produce updated prototypes, allowing for faster product development cycles and design improvements.
- Integration with CAD/CAM Software:CNC routers seamlessly integrate with CAD/CAM software, enabling streamlined design-to-production workflows. Designers can create digital designs, generate toolpaths, and directly transfer them to the CNC router, ensuring accuracy and eliminating manual programming errors.
- Customization: CNC routers offer customization capabilities, allowing for personalized designs and unique creations. They can produce one-off pieces or tailor designs to specific customer requirements, enhancing customer satisfaction and product differentiation.
- Waste Reduction: CNC routers optimize material usage by minimizing waste. With precise cutting and nesting capabilities, they maximize the utilization of materials, reducing material costs and minimizing environmental impact.
Future Trends and Innovations of CNC routers:
- Automation:CNC routers will become more autonomous, reducing the need for manual intervention and improving efficiency.
- IoT Integration:CNC routers will be connected to the Internet, allowing for remote monitoring, data collection, and predictive maintenance.
- Additive Manufacturing Integration: CNC routers will work together with 3D printing, enabling the creation of complex components using a combination of subtractive and additive processes.
- Improved Precision and Speed: Future CNC routers will offer even higher levels of accuracy and faster machining capabilities.
- Multi-Axis Machining: CNC routers with multiple axes will become more common, allowing for complex cuts and contours.
- Expanded Material Compatibility:CNC routers will be able to work with a wider range of materials, including advanced composites and alloys.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality Integration:Virtual and augmented reality technologies will be used to enhance design visualization and simulate machining processes.
- Sustainable Practices: CNC routers will adopt more sustainable practices, such as reducing waste and energy consumption.
- Machine Learning and AI Optimization:Machine learning and AI techniques will optimize CNC router operations for improved efficiency and quality.
- Collaboration and Connectivity: CNC routers will be more connected and integrated with other machines and systems, streamlining production workflows.
These simplified trends and innovations highlight the potential advancements that may shape the future of CNC routers, contributing to increased automation, precision, material compatibility, and sustainability.
Conclusion:
CNC routers are transforming the manufacturing landscape with their precision, efficiency, and versatility. As technology continues to advance, CNC routers are poised to play an increasingly vital role in various industries. By embracing these powerful machines, manufacturers can unlock new levels of productivity, quality, and innovation in their operations.