Top 5 Design Tips for Stronger 3D Printed Parts
Whether you’re creating prototypes or functional end-use components, ensuring strength and durability in your 3D printed parts is essential. Good design can significantly enhance part performance, reduce failure rates, and make your prints more reliable. Here are the top 5 design tips to help you get stronger, more resilient 3D printed parts.
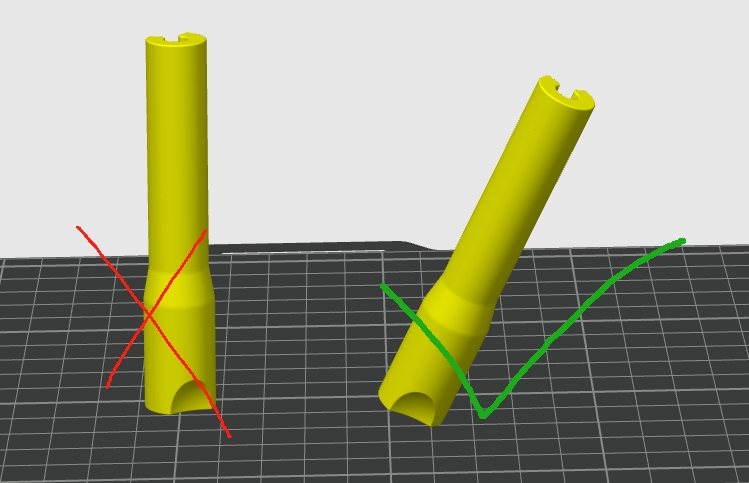
- Optimize Print Orientation
Layer adhesion is typically the weakest point in any 3D printed part. To maximize strength, orient your part so that the layers run perpendicular to the direction of the applied forces. For example, if the part will endure vertical stress, consider printing it lying down so the layers stack horizontally relative to the stress.
Pro Tip: Use simulation tools to predict stress points and align your model accordingly.
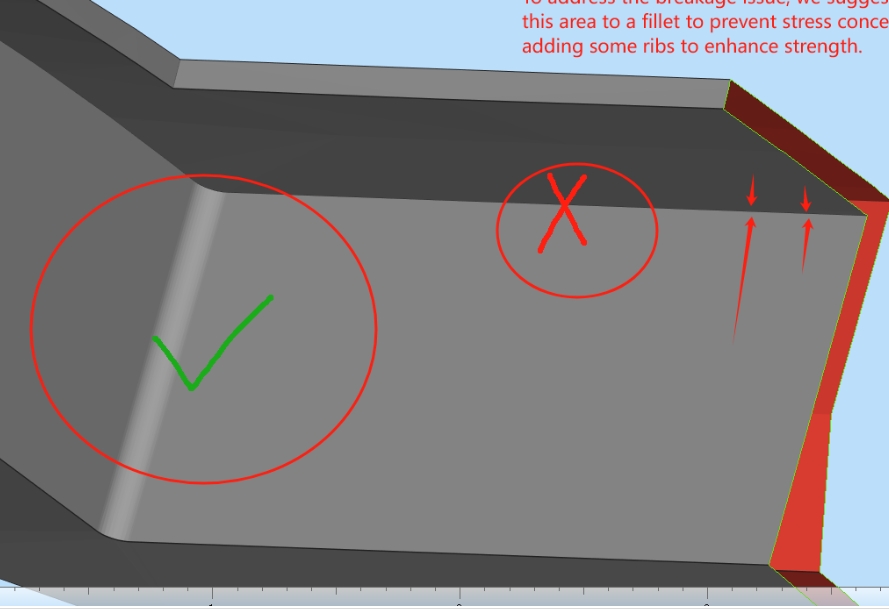
- Use Fillets Instead of Sharp Corners
Sharp corners create stress concentration points which can lead to cracking. Adding fillets (rounded edges) not only improves the strength by distributing stress more evenly but also enhances the printability by reducing potential printing errors.
Pro Tip: A fillet radius of 1-2 mm is often sufficient for improving part integrity.
- Increase Wall Thickness and Infill Density
One of the simplest ways to strengthen your part is by adjusting wall thickness and different infill settings. A thicker shell and higher infill percentage will create a sturdier structure. However, this also increases material use and print time, so find a balance based on your part’s function.
Pro Tip: For functional parts, use at least 2 mm wall thickness and 50% infill or higher.
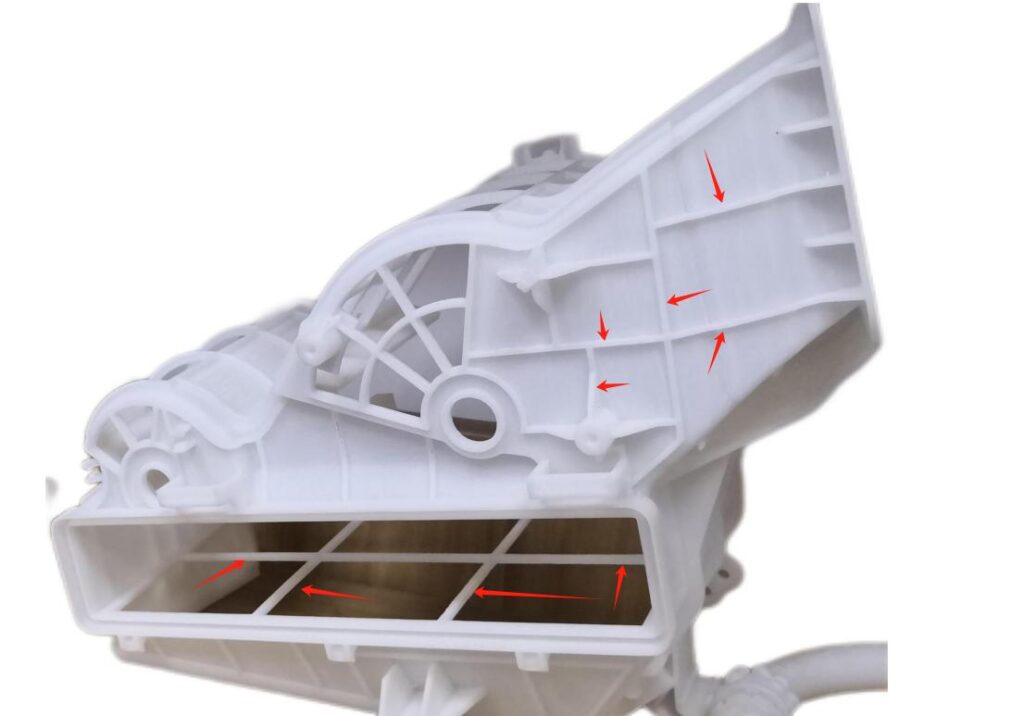
- Add Ribs and Gussets for Structural Support
Instead of just increasing infill, adding structural features like ribs (vertical walls) and gussets (triangular supports) can reinforce weak sections without significantly increasing weight or print time. These features are especially helpful in load-bearing areas.
Pro Tip: Integrate ribs along flat surfaces or near holes to reduce flex.

- Choose the Right Material
Material selection is key. PLA might be easy to print, but it lacks the toughness of materials like PETG, ABS, or Nylon. If you’re printing functional parts that will be stressed, exposed to impact, or require flexibility, choose a material that meets those needs.
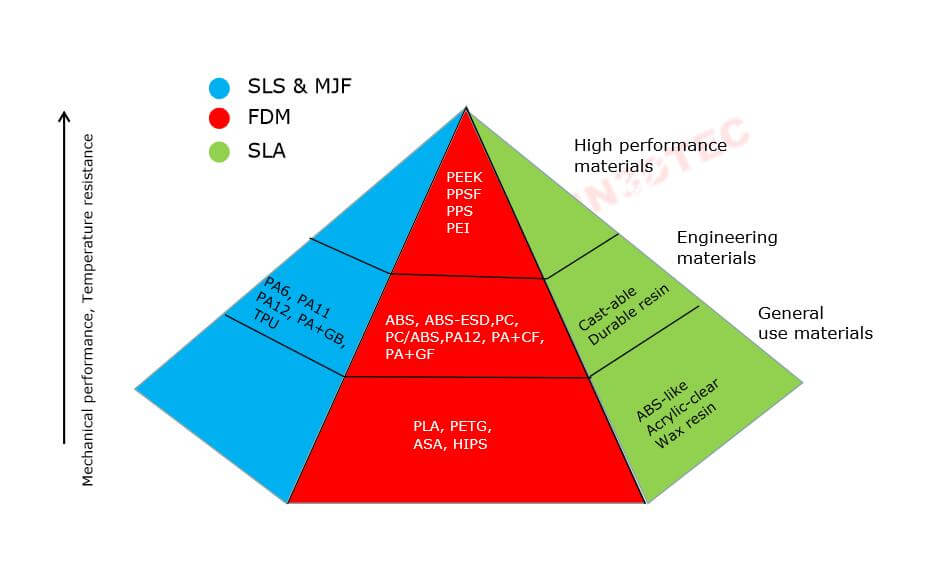
Pro Tip: Consider carbon fiber-reinforced filaments for high-stress, lightweight applications.
Read more: Material Select Guide for 3D Printing
Conclusion
Stronger 3D printed parts begin with smarter design choices. By carefully considering print orientation, geometry, and material selection, you can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of your parts. Have a part you’re designing? Contact us to review your files and recommend the best settings and materials for maximum strength.