Metal 3D Printing Technologies: SLM vs. DMLS
When it comes to metal 3D printing, there are two leading technologies that are used: selective laser melting (SLM) and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS). Both of these technologies have their own advantages and disadvantages, which is why it’s important to know the difference between the two before deciding which one is right for your project. In this blog post, we will look at both SLM and DMLS to help you make an informed decision.
What is SLM?
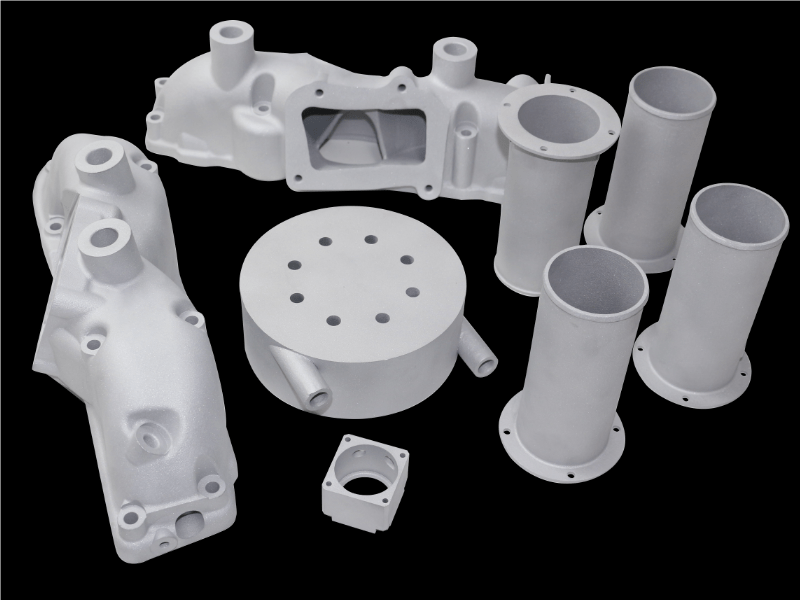
SLM is a type of 3D printing technology that uses a laser to melt metal powder layer by layer until the desired shape is created. One of the main advantages of SLM is that it can be used to create complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to create using traditional manufacturing methods.
Additionally, SLM allows for high precision and repeatability, making it ideal for producing small batches of parts with tight tolerances. However, SLM is limited by the fact that it can only be used with metals that have a low melting point, such as aluminum and titanium, whereas DMLS can cover a wider range of material as we will see below.
What is DMLS?
DMLS is another type of 3D printing technology that uses a laser to fuse together metal powder layer by layer. Unlike SLM, DMLS can be used with metals that have a high melting point, such as stainless steel and cobalt chrome.
Also, DMLS offers a higher build rate than SLM, making it ideal for large-scale production runs. Perhaps the most significant limitation is the initial cost of the machines and materials. However, you do not need to worry about it when you rely on a professional service like the one offered by IN3DTEC.
Yet, we have to mention that some people may have issues with the porous surface finish, but this is something that is easily corrected through processes such as sandblasting, bead blasting, polishing, and powder coating, among others depending on the specific needs. And this is also part of our service.
Applications of DMLS
- Prototyping: DMLS can be used to quickly prototype and manufacture parts for a variety of applications, from medical equipment to aerospace components. Its ability to go from 3D CAD design to functional part allows for faster development time and improved short-term production capabilities.
- Rapid Tooling: With the precision and accuracy of DMLS, it can be used to quickly produce metal molds and tooling for injection molding, die casting, and other manufacturing processes. This is especially useful for low-volume production runs or when quick turnaround times are required.
- Metal Consolidation: DMLS also offers metal consolidation by combining multiple parts into one single component with improved strength, density and weight reduction over traditional processes such as welding or brazing. It can be used in a variety of industries such as automotive, aerospace and medical where weight reduction is critical in the design process.
- Functional Parts: The layer-by-layer additive manufacturing process of DMLS provides complex geometries that would not be possible with traditional manufacturing methods such as complicated lattices with high strength-to-weight ratio features or cooling channels in heat exchangers which can reduce assembly costs when compared to traditional parts made up of many individual components.
- Repair & Replacement: Due to its ability to provide near net shape parts with complex geometries, 3D printing enables the repair of existing components by being able to replace worn or broken pieces quickly and cost effectively without having to search for replacements or custom order one piece at a time from a machinist shop.
- Medical Implants: Highly customized metal implants manufactured using DMLS offer excellent fitment characteristics due their unique geometrical flexibility which allows them to better accommodate patient anatomy compared to standard off-the-shelf implants. Additionally, they can be produced very quickly which is important in emergency cases where time is critical factor in helping save lives.
Some final words
When choosing a metal 3D printing technology for your project, it is important to understand the difference between SLM and DMLS. Both technologies have their own advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to select the one that best meets your needs. If you need help with metal 3D printing, feel free to contact us today—we’re always happy to help!