Rubber Molding: Three Techniques for Creating Rubber Molded Parts
Introduction:
Rubber molding is a versatile manufacturing process used to create a wide range of rubber products with different shapes, sizes, and properties. This process involves shaping liquid or semi-liquid rubber materials into molds and allowing them to cure or solidify. In this blog post, we will explore three common techniques for producing rubber molded parts and their respective advantages and applications.
1. Compression Molding:
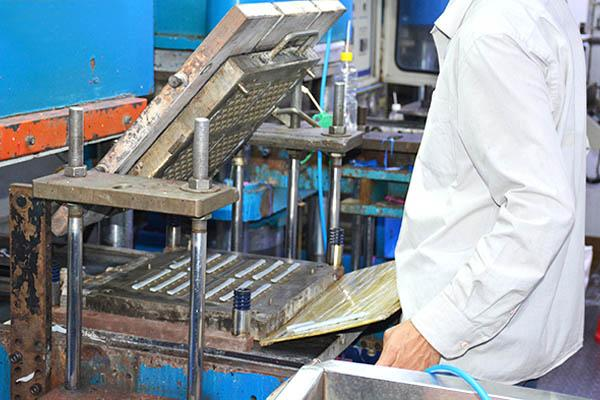
Compression molding is one of the oldest and most widely used methods for rubber molding. It involves placing a pre-measured amount of raw rubber material, also known as a “charge,” into a heated mold cavity. The mold is then closed, and the rubber is compressed under pressure until it fills the mold cavity and takes its desired shape. Heat and pressure are maintained until the rubber cures or vulcanizes.
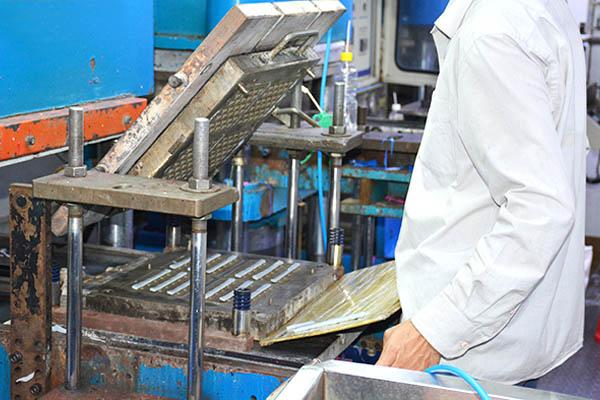

Advantages of Compression Molding:
– Suitable for a wide range of rubber materials, including high durometer and high-temperature compounds.
– Capable of producing large and complex parts.
– Cost-effective for low to medium production volumes.
– Offers excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
– Ideal for rubber-to-metal bonding applications.
Applications of Compression Molding:
– Gaskets and seals
– O-rings
– Automotive components
– Industrial parts
2. Injection Molding:
Injection molding is a highly automated and efficient rubber molding technique. It involves injecting a precisely measured amount of liquid rubber material, called a “shot,” into a closed mold cavity under high pressure. The rubber is then allowed to cool and solidify, after which the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected.
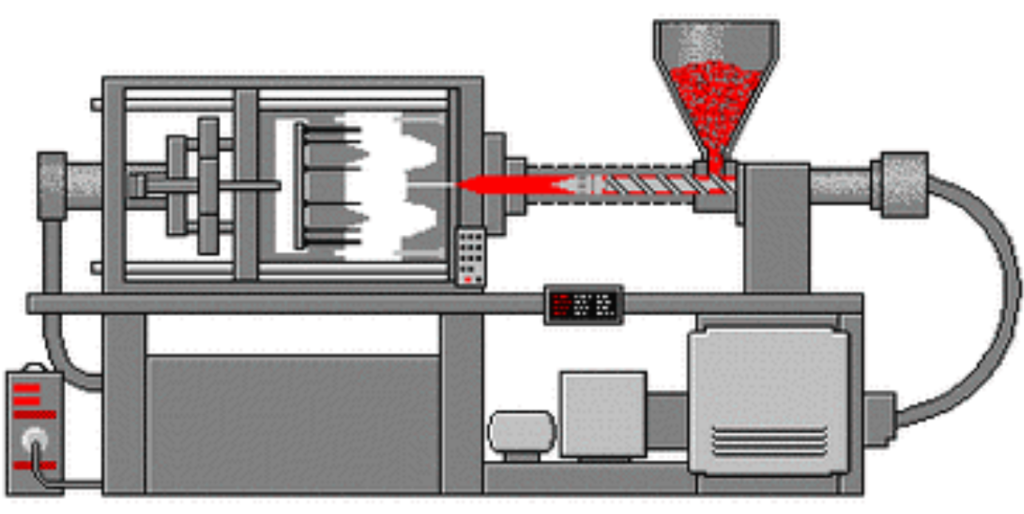
Advantages of Injection Molding:
– Enables high production volumes and short cycle times.
– Provides tight dimensional control and repeatability.
– Offers the ability to produce complex geometries and intricate details.
– Allows for the use of various rubber materials, including liquid silicone rubber (LSR) and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE).
– Well-suited for overmolding and insert molding applications.
Applications of Injection Molding:
– Medical devices and components
– Seals and gaskets
– Consumer electronics
– Automotive parts
- Transfer Molding:
Transfer molding is a hybrid process that combines elements of compression molding and injection molding. It involves preheating rubber material in a separate chamber, known as a “pot,” before transferring it into a closed mold cavity through a runner system. Pressure is applied to force the rubber into the mold cavities, where it cures and solidifies.
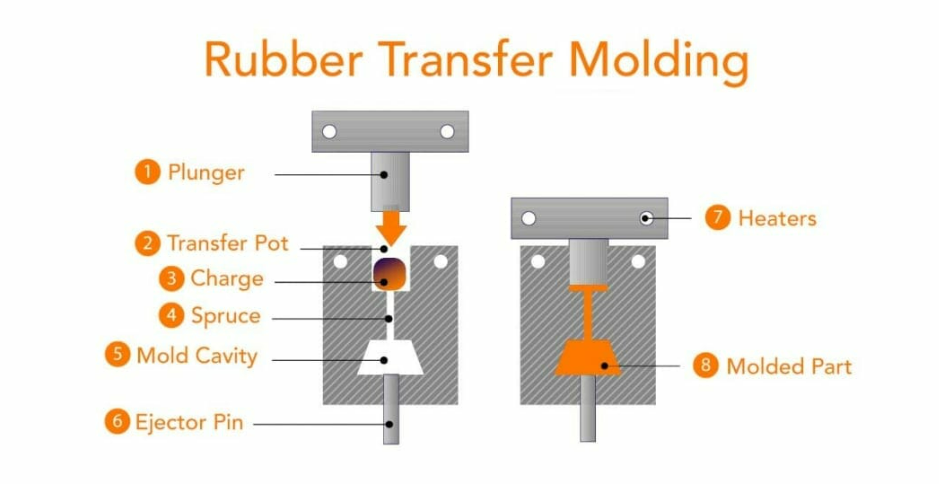 (image from qualiform)
(image from qualiform)
Advantages of Transfer Molding:
– Enables the use of a wide range of rubber materials, including heat-sensitive compounds.
– Offers shorter cycle times compared to compression molding.
– Provides better control over material flow and minimizes flash formation.
– Suitable for producing intricate and small-sized parts.
– Allows for consistent part quality and dimensional accuracy.
Applications of Transfer Molding:
– Electrical connectors and components
– Seals and gaskets
– Automotive parts
– Aerospace components
Conclusion:
Rubber molding provides a reliable and efficient means of manufacturing rubber molded parts. Whether you choose compression molding, injection molding, or transfer molding, each technique offers its own advantages and applications. Compression molding is versatile and cost-effective, while injection molding allows for high production volumes and intricate designs. Transfer molding combines the benefits of both compression and injection molding. By understanding the differences and capabilities of these three techniques, you can select the most suitable rubber molding method for your specific project requirements and achieve high-quality rubber molded parts.