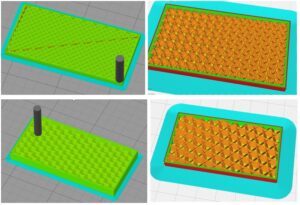
Benefits of metal 3d printing
Aluminum, Stainless Steel 316L, Maraging Steel (MS1), Titanium(Ti64)
All uploads are secure and confidential
What is the performance of metal 3D printed parts compared with traditional processed ones? What materials are available in metal 3d printing? In which industries are metal printing can be used? How to design products based on its printing performance?
With the development of laser-based powder bed fusion, the first technology for metal Additive Manufacturing was established. Today we know more than 18 different metal 3D printing processes, so it is necessary to understand its performance and possibilities before choosing one.
Table of contents
It takes around 10 minutes to read.
>>Types of metal printing
>> Case Studies
>> Supported materials
>> Mechanical performance、Tolerance & smoothness
>> Surface finishes
>> Benefits & Limitations
>> Free design tips
>> Types of metal 3D Printing
Category | Technology & Definition | Photo |
Powder | 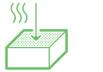 | |
Laser Beam Powder Bed Fusion |  | |
Binder Jetting |  | |
Powder Metallurgy Jetting |  | |
Powder Feed Laser Energy Deposition |  | |
Cold spray |  | |
Wire | Wire Arc / Plasma Arc Energy Deposition |  |
Liquid Metal Printing |  | |
Sheets | Ultrasonic Welding |  |
Rods | Friction Deposition |  |
Dispersion | Nanoparticle Jetting |  |
Filament | Metal Filament Modeling |  |
Pellet | Metal Pellet Fused Deposition Modeling |  |
Image Courtesy of AM POWDER INSIGHT DE
Among the above technologies, every technology has its advantages, so it is hard to say which one is good or bad. The most popular technologies are Binder jetting, DMLS, EBM, and SLM, free from residual stresses and internal imperfections.
>>Case Studies
Automotive
Metal printed cooling jacket, Material in Alsi10Mg with sand blasting and heat-treatment
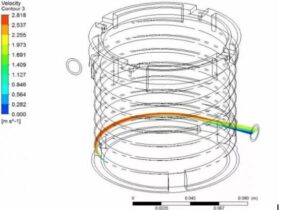


Aerospace
Turbine

Medical
Surgical Implant, Medical-Ti64, Design by Sachith Fernando, Ataintl, printed at IN3DTEC factory

Jewelry
Titanium, SS316, Al10SiMg, Designed by Rawan Alderjem, Printed at IN3DTEC factory

Tooling
Stainless Steel 316

>> Supported materials
So far, there are almost more than 15 materials are available in the market, such as Aluminum-AlSi10Mg, Bronze, Copper, Maraging Steel(18Ni300), Stainless Steel(420, 316L, 15-5PH, 17-4PH), Inocel(718, IN625, GH3536), Titanium-Ti6Al4V, Silver, and more.
Please visit the below link to check the available materials’ TDS from IN3DTEC.
https://www.in3dtec.com/material-data-sheets/
>>Mechanical performance、Tolerance & Smoothness
| AlSi10Mg-AL | SS 316L | Maraging Steel-18Ni300 | Titanium-Ti64 | |
| Mechanical Properties(As printed) | ||||
| Density (g/cm3) | ≥2.65 | ≥7.9 | ≥8.0 | ≥4.4 |
| Tensile strength Mpa | 430±30 | 637±50 | 1150±100 | 1150±70 |
| Yield Strength Mpa | 270 | 550±50 | 1050±100 | 1000±50 |
| HRC | 140±20 HV5/15 | 215±10 HV5/15 | 35±3HRC | 360±30 HV5/15 |
| Elongation after Fracture(%) | 3±1 | 34±5 | 12±3 | 8±2 |
| Mechanical Properties(Heat Treated) | ||||
| Density (g/cm3) | ≥2.65 | ≥7.9 | ≥8.0 | ≥4.4 |
| Tensile Strength Mpa | 350±50 | 600±50 | 1950±100 | 1050±70 |
| Yield Strength | 240±30 | 500±50 | 1900±100 | 950±50 |
| HRC | 75±20 HV5/15 | 190±10 HV5/15 | 53±3HRC | 330±30 HV5/15 |
| Elongation after Fracture(%) | 6±1 | 45±5 | 4±2 | 12±2 |
Roughness as built: Ra7-9
Tolerance:Length within 100mm +/- 0,1mm; length >100mm, 100*0.1%mm
CNC Machining: When tighter tolerances than the standard ± 0.1 mm are required, machining is employed as a finishing step.
Heat-treatment: To improve the material properties of the part.
Polishing: Certain applications require a smoother surface than the standard RA 7 μm of as-printed.
>> Surface finishes
CNC Machining: For tighter tolerance than +-0.1m are required.
Sand-Blasting: To remove the visible layers on the surface
Electropolishing: To make a super smooth surface
Regular/Normal polish: By hand, to get a Roughness like machined parts
Anodizing, Plating: For parts that can be polished well, make a uniform or protection surface coating.
>> Benefits and limitations
Benefits:
+ Free-design your parts in a complex structure
+ Good accuracy and fine details
+ Various materials
+ Time and cost save for low-volume parts
Limitations:
– Cost is higher than CNC for simple parts
– Support structures should be paid more attention to
– Roughness is higher than CNC
> Free Design Tips
| Position | Tips |
| a | Minimum wall thickness 0.5mm |
| b | Fonts minimum thickness 0.5mm |
| c | Fonts height or depth 0.5mm |
| d | Minimum hole diameter 0.8 mm |
| e | Minimum Gap 0.5mm |
Thread: Tapping the thread by CNC after the printing is recommended
Assemble gap: 0.15mm at each side is necessary for parts to need assembly